Sideways often occur in the forex market. Even though it looks sluggish and boring, there are still ways to gain profit from this condition. How so?
Sideways markets, also known as range-bound markets, occur when the price trades within a reasonably stable range without forming any distinct trends over some time. The price action instead oscillates in a horizontal range or channel, with neither the bulls nor bears taking control of prices.
This means there is no clear upward or downward trend in the price. Instead, the price tends to move back and forth between two specific levels, the support and resistance levels.
Sideways markets can frustrate traders as they offer fewer opportunities to make big profits. However, making money in sideways markets is still possible with the right approach.
Whether you're an experienced or a novice trader seeking to expand your trading experience, understanding how to trade in sideways markets effectively can be your ticket to consistently successful trading.
Steps to Trade on Sideways Markets
Trading in sideways market conditions requires a different approach than in trending markets. In general, here are the steps for trading on a sideways market:
- Identify the sideways market. This can be done by looking at price charts and identifying horizontal support and resistance levels. If the market trades within a well-defined range, it will likely be in a sideways trend.
- Define support and resistance levels. Once you have identified the sideways area, you must define the upper and lower price ranges. This will help you to identify entry and exit points for your trades. Support levels are the prices at which buyers will likely step in and prevent the market from falling further, while resistance levels are the prices at which sellers will likely step in and prevent the market from rising further.
- Use technical indicators. Technical indicators can help you identify entry and exit points for your trades. Some popular technical indicators for trading sideways markets include Bollinger Bands, Moving Averages, and Relative Strength Index (RSI).
- Have a risk management plan in place. No matter what market conditions you are trading in, it is essential to have a risk management. This will help you to limit your losses in the event of a trade going against you. Your risk management plan should include things like stop-loss orders and position sizing.
Trading Strategy In Sideways Markets
This strategy is relatively easy for anyone to use. However, before using this strategy, there are several necessary settings that traders need to pay attention to to get maximum results:
- Pair: Major pairs are preferred.
- Time frames: All time frames can work.
- Indicators: Relative Strenght Index (RSI)
Entry Setup
- Identify support and resistance lines on the chart. Look for areas where the price has bounced multiple times in the past.
- Use the RSI indicator to identify overbought and oversold conditions.
- Buy entry signal:
- The price tests the support line and fails to break below it.
- The RSI indicator is in oversold territory (below 30).
- Enter a long position around the rebound area at the support level.
- Sell entry signal:
- The price tests the resistance line and fails to break above it.
- The RSI indicator is in overbought territory (above 70).
- Enter a short position around the rebound area at the resistance level.
For a more precise understanding, please refer to the chart below.
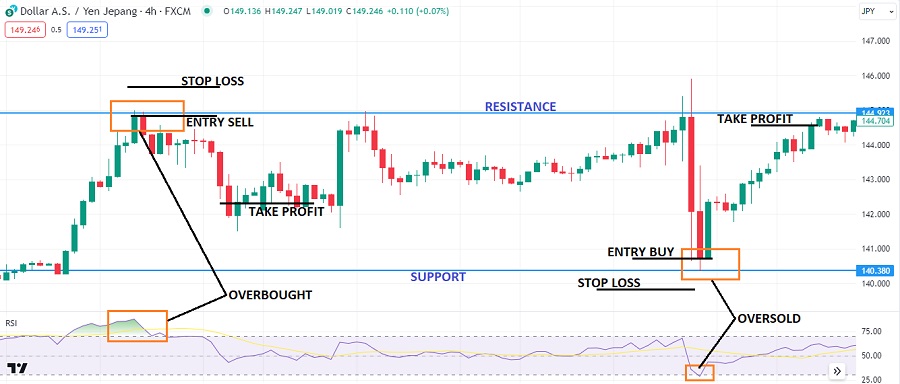
In the example above, the USD/JPY pair is experiencing a sideways trend, with price bouncing off the support and resistance areas. The RSI indicator can identify entry opportunities when the price is overbought and oversold.
Stop Loss and Take Profit
Setting stop loss and taking profit orders for all your trades is vital, regardless of the market trend. This will help to limit your losses and protect your profits. A good rule of thumb is to use a risk-reward ratio of 1:2. For every pip you risk on a trade, you expect to make two pips in profit.
For example, if you place a stop loss ten pips below your entry price, you should put your take profit level 20 pips above your entry price. This will give you a risk-reward ratio of 1:2. You can also use other methods to set your stop loss and take profit levels, such as Fibonacci retracement or pivot points.
Indicators for Sideways Trading
Apart from RSI, there are indicators that can identify overbought and oversold conditions, momentum shifts, and volatility contractions to help you find trading opportunities in sideways markets:
- Stochastic Oscillator: The Stochastic Oscillator is a momentum indicator that compares the closing price of a security to a price range over a given period. The oscillator's sensitivity to market movements is inversely proportional to the period used in its calculation.
- Bollinger Bands: Bollinger Bands are a volatility indicator that uses a moving average (typically the 20-day simple moving average) and two standard deviation bands plotted above and below the moving average.
- Average Directional Index (ADX): The ADX is a non-directional indicator of the trend's strength. It is displayed as a line ranging from 0 to 100, with higher readings indicating a stronger trend.
- Commodity Channel Index (CCI): The CCI is a technical analysis indicator that measures the current price level relative to an average price level over a given period. The CCI is calculated as the (current price - average price) divided by the mean deviation of the price over the given period.
- William's Alligator Indicator. The William's Alligator indicator detects sideways through a sideways line flow. A trend forms if the flow moves in the opposite direction. However, if the flow moves overlapping, then sideways is occurring in the market.
Tips During Sideways Market
- Use small timeframes. Sideways markets are often characterized by low volatility, making it difficult to profit in higher timeframes. Trading in smaller timeframes, such as the 1-minute or 5-minute timeframe, can give you more opportunities to profit from small price movements.
- Take minor positions. To anticipate unfavorable breakouts that are usually followed by high volatility, it is essential to trade with smaller positions.
- Be patient. Sideways markets can be dull, and it can be tempting to make impulsive trades. However, it is essential to be patient and wait for the right trading opportunities to present themselves.
Pros and Cons of Trading on Sideways Markets
Trading in sideways markets, also known as range-bound or consolidation markets, has advantages and disadvantages.
Pros of Trading on Sideways Markets:
- Lower volatility. Sideways markets are characterized by lower volatility, which can reduce the risk of losses.
- More opportunities to profit from small price movements. Sideways markets often have smaller price movements, providing more opportunities to profit from small price changes.
- It is more straightforward to identify trading opportunities using technical indicators. Technical indicators can help identify trading opportunities in sideways markets, as the price will likely consolidate within a well-defined range.
Cons of Trading on Sideways Markets:
- Lower potential profits. Sideways markets have lower potential profits, as the price is not moving in a clear direction.
- Breakout risks. Sideways markets can make it more challenging to identify the trend, leading to losses if the price breaks out of the range.
- More time-consuming. Sideways markets can take more time so traders must be patient and wait for the right trading opportunities.
Who Is Sideways Market Meant for?
Here are some specific types of traders who may be well-suited for trading in sideways conditions:
- Range traders: Range traders look for markets trading within a defined range and look to buy at support levels and sell at resistance levels.
- Day traders: Day traders typically enter and exit trades within the same day. This can be a good way to trade sideways markets, allowing traders to take advantage of short-term price movements.
- Swing traders: Swing traders typically wait for opportunities around highs and lows. Since the price forms relatively consistent highs and lows during a sideways market, swing traders could read the signals much more easily.
- Options traders: Options traders can use various strategies to profit from sideways markets. For example, they can buy straddles or strangles, which are options strategies that profit when the market moves within a certain range.
In conclusion, sideways markets can be challenging to trade but profitable if you have the right strategy. Traders with a good understanding of technical analysis can identify support and resistance levels and other technical patterns to take advantage of the ranging market.
Sideways markets are common in forex, especially when there is little activity or supply and demand. Supply and demand are fundamental factors and their interaction is crucial because they mutually influence each other. See "Supply and Demand Concept in Forex Market" for more information.

 Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS
Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS Free FOREX Virtual Private Server
Free FOREX Virtual Private Server MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500
MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500 Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus
Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024
Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024 Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise
Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise $1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients
$1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus
Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest
Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance
Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance