Margin in forex might be a hassle to unravel for there are so many things to learn about it. This article will answer all questions you have about it in a simple way.
What is the margin in forex? And why it's important for your trading activity?
Understanding margin is not something traders can ignore. But, when we talk about margin, there is more than meets the eye.
What is Margin in Forex?
The term margin is often mentioned in forex trading. It's not a new concept. However, novice traders might not fully understand the meaning of margin.
The margin in forex is not the cost or fee you pay to trade. It's the collateral you (as a trader) need to have to cover some risk you generate for the broker.
Usually, the margin is a fraction of trading positions and expressed as a percentage.
Your margin amount can influence your trading outcome with significant differences in profits and losses.
For example, say a broker required a margin of 10%. That means for every $10 you want to trade, you have to supply $1 of margin. In this case, we could leverage our trade to 1:10.
Some brokers conveniently offer interest on margin for their clients. That's why it's important to understand the forex margin requirement before choosing a broker.
Usually, the trading platform will show traders how much equity they have alongside their balance and free margin. Here is an example of where it is listed in the popular trading platform MT5. Click the 'Trade' tab, and this information will appear below the charts.
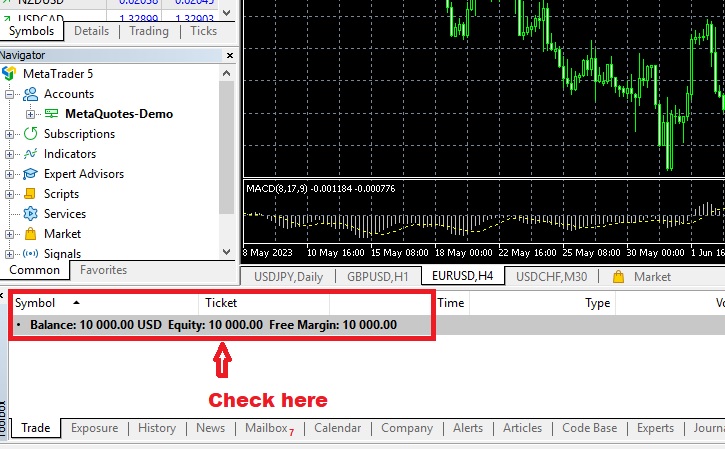
How Do You Calculate Forex Margin Requirement?
Using margin in forex means you have to calculate your margin requirement. It is different according to what pair of currency you are staking a position in vs. the currency you used in your account.
For example, you are trading GBP/USD while your account currency is USD. You decide to take a position with 10,000 units of currency.
This means you buy 10,000 GBP (the base currency) against 100,000 USD (the quote currency). Since your account currency is USD, your broker will calculate the margin requirement in USD.
You need to calculate your margin requirement in GBP/USD. You can use this formula to find out.
(GBP/USD exchange rate) x contract size x % leverage x 100
Say the exchange rate of GBP/USD today is 1.38, your contract size is 1000, and your broker uses a leverage of 1:200 or 0.5%. Your forex margin requirement will be.
1.38 x 200 x 0.5% x 1000 = 1656
To save you some time, you can use a margin calculator to find out how much is your margin requirement per trade.
What is the Relationship between Leverage and Margin?
When trading with margin, you must also be careful with leverage. The higher the leverage, the smaller the margin. It will automatically lead to a condition where you trade with great risk exposure.
For example, if you choose high leverage that means you can lose all of your money instantly because even small price movements can bring you big losses, provided the price is moving against your trade.
The relationship between margin and leverage is inverse. The required margin decreases as the leverage ratio increases, and vice versa. Higher leverage allows traders to control larger positions with less margin required, which means they can potentially make larger profits than their initial investment.
High leverage is often also responsible for the urge to overtrade, as it can reduce the margin requirement. For some rookie traders, it creates the illusion of having a big amount of equity at their disposal.
For example, if a trader has a leverage ratio of 1:100, they can control a position that is 100 times larger than their margin deposit. In this case, if they deposit $100 as margin, they can open trades worth $10,000.
That means traders can take more positions with less money. When things go well, borrowed money can increase the returns, but, if things go badly, traders could lose their trades much quicker.
If they aren't careful, they will get margin calls sooner than those using smaller leverage.
Free Margin vs Used Margin, What's the Difference?
You can use free margin to open new trading positions in your trading account. The amount of your free margin can be subtracted from your account equity.
Side note, equity is the sum of your account balance and any unrealized profit or loss from any open positions. If you aren't holding any position, all the balance in your account can be considered the free margin.
Suppose you have a $10,000 margin with $50 unrealized profit but use $4000 to open a position. That means your free margin is $6000. You can use this money to open another position or keep it in your account. This makes your equity $10,050.
New traders might not know the difference between a used margin and a free margin. The used margin is the margin itself. The amount of used margin can be seen from your capital and leverage ratio. For example:
Suppose you trade one standard lot with a $100,000 contract value. You open a position in EUR/USD with 1:100 leverage at 1.1071. To calculate the used margin, use this formula.
Used margin = (contract value) x (lot) x (margin %) x current exchange value
Therefore,
($100,000) x 1 x 1% x 1.1071 = $1,107.1
$1,107.1 is your used margin.
What is a Margin Call?
It is not uncommon for brokers to initiate a margin call. But what is a margin call? And how does it affect margin in forex trading?
A margin call is a warning system from your broker that is activated when your loss reaches the amount of your equity. The broker will close part of the position until the margin requirement is met again.
So, how does it work?
Suppose you choose a $1000 margin as a security deposit with your broker. Suddenly your position in the market worsens, and your total loss reaches $1000. That's when your broker might initiate a margin call. They will instruct you to either deposit more money or close the position.
Some things might cause margin call:
1. Overconfidence
Some traders who made hefty profits will get a boost of confidence, which is good. But those with bad money management might be tempted to open more positions carelessly.
This move can be a mistake that might lead to a margin call. Taking risks is allowed when you have a good analysis and trading strategy to execute it. But if you're not, it's better to take a step back and revise your strategy.
The result of being overconfident is overtrading. When a trader opens a position based on emotion, they ignore the market analysis. This might lead them to a margin call and lose all their profits.
2. Trading Without Stop Loss
Trading without stop loss can be dangerous, especially for novice traders. If you let your trading positions close with considerable loss, you might experience a cumulative margin call.
Your losses will eat up your free margin, eventually leading to a margin call. In short, do not trade without a clear strategy and strong analysis.
How to Avoid Margin Calls?
Now that you know about margin calls, you might ask yourself, how do I avoid it? There are a few steps you can take to avoid a margin call.
- Choose Major Currency Pairs
Major currency pairs have low spreads and high liquidity. This makes them easier to be analyzed with minimum extreme volatility. You should choose major currency pairs such as GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, and EUR/USD. - Risk Management
Managing risk is important if you want to avoid a margin call. That means you must be aware of your trading account's available funds. Then, make realistic movements to prevent your losses. - Manage Your Emotion
Emotion can be influential when using margin in forex trading. If you want to avoid margin calls, you can't be overreacting when you lose a trade. Keep your emotion in check. If you don't, it might lead to overtrading and increase the risk of margin calls. - Learn from Mistakes
As bad as it sounds, most traders have experienced margin calls. What you need to do is to avoid repeated margin calls by continuing to evaluate your trading style. It might seem trivial, but monitoring your journey and trading progress is helpful. - Hedging Strategy
Learning about hedging strategy can be useful to avoid margin calls. You can do this by opening two positions in opposite directions simultaneously. Let's say your Buy position is losing because the price keeps declining from your entry point. Consider opening a Sell position on the same pair.
The main idea is to offset the loss you get from your Buy position. Make sure to take notes of the correlation between currency pairs. It is very dangerous to misunderstand the correlations, eventually leading to cumulative margin calls.
Final Words
While it's true that using margin in forex might amplify the risk, the rewards can be just as big.
The risk of using margin in forex might expose your account to significant losses. Not to mention the stress you get due to the implications of market volatility. Don't forget that your account can also be subject to a margin call.
Nonetheless, using margin in forex trading is undeniably effective in growing your account value exponentially.
There are several misconceptions about trading with margin. Are they real or just myths? Find more about them here.

 Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS
Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS Free FOREX Virtual Private Server
Free FOREX Virtual Private Server MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500
MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500 Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus
Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024
Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024 Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise
Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise $1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients
$1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus
Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest
Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance
Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance













11 Comments
George
Jul 7 2023
Hey, let's talk about scalping as a trading strategy and whether it's possible to do it without using a stop loss. So, we all know that trading without a stop loss can be quite risky, especially for beginners. You don't want to find yourself in a situation where your trading positions keep accumulating losses and eventually lead to a margin call. That's not fun at all!
But here's the thing I'm curious about: Is it ever possible to engage in scalping without relying on a stop loss? I mean, can traders solely rely on their sharp strategies and strong analysis to navigate the market and avoid significant losses? It's an interesting idea, but I wonder if it's practical or if it's just wishful thinking.
What do you think? Have you come across any successful scalpers who swear by trading without a stop loss? Or do you believe that having a clear strategy and using a stop loss go hand in hand when it comes to managing risks in scalping?
Hector
Jul 11 2023
@George: Hey, I totally get your curiosity about scalping as a trading strategy and the possibility of doing it without a stop loss. Trading without a stop loss can indeed be risky, especially for beginners. We definitely don't want to end up in a margin call situation with accumulating losses.
Now, the question is, can scalping be done without relying on a stop loss? It's an intriguing thought, but let's weigh the practicality of it. While it's true that scalpers rely on their sharp strategies and analysis to make quick trades, having a stop loss is generally considered an essential risk management tool.
In the end, having a clear strategy and using a stop loss typically go hand in hand, especially in scalping where trades are executed rapidly. It's always recommended to prioritize risk management and protect your trading capital. So, unless you have extensive experience and a proven track record, incorporating a stop loss in your scalping strategy is generally a wise decision to manage risks effectively.
Justin
Jul 13 2023
Imagine you're a trader who has just made substantial profits. Your confidence is soaring, and it feels like you're on top of the world. However, there's a catch: you notice that some traders with poor money management skills are falling into a common trap. They let their newfound confidence drive them to open more positions recklessly, without proper analysis or strategy.
Now, here's where things can take a turn. This impulsive behavior often leads to a margin call, resulting in potential losses and undoing all the hard-earned profits. It's a classic case of overtrading, driven by unchecked emotions and a disregard for proper market analysis.
Knowing this, how do you ensure that you can control your emotions in trading and avoid falling into the overtrading trap? Share your strategies and experiences on how you keep a level head, stick to your analysis and trading plan, and avoid being swayed by emotions that can cloud your judgment. Let's dive into the world of emotional control in trading and learn from each other's stories.
Johanna
Jul 14 2023
What factors contribute to reducing the likelihood of a margin call when ing major currency pairs for trading? I understand that major currency pairs are characterized by low spreads and high liquidity, making them easier to analyze with minimal extreme volatility. Could you provide more insights into why major currency pairs like GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, and EUR/USD are considered preferable in terms of reducing the risk of a margin call? How does the liquidity and stability of these major pairs contribute to minimizing the potential for extreme price movements that could trigger a margin call?
Brianna
Jul 15 2023
@Johanna: When trading major currency pairs like GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, and EUR/USD, several factors contribute to reducing the likelihood of a margin call. These pairs are commonly preferred for their liquidity and stability, which play a significant role in minimizing the potential for extreme price movements that could trigger a margin call.
The high liquidity of major currency pairs ensures that there is a large volume of buyers and sellers in the market. This means that orders can be executed quickly and at a desired price, reducing the risk of slippage and unexpected price gaps. Liquidity also allows traders to enter and exit positions more efficiently, enhancing their ability to manage risk effectively.
Moreover, major currency pairs typically have lower spreads compared to exotic or less-traded pairs. The lower spreads make it easier to enter and exit trades without incurring substantial transaction costs. This can be crucial in reducing the impact of spreads on overall trade profitability and minimizing the risk of margin calls.
Major currency pairs are also known for their relative stability, characterized by consistent price movements and well-established trends. This stability makes them more predictable and easier to analyze using technical and fundamental analysis techniques. Traders can make informed decisions based on historical price patterns, economic data, and geopolitical factors, reducing the chances of unexpected market volatility that could trigger a margin call.
Brandy
Nov 23 2023
The article emphasizes the peril of trading without implementing a stop loss, especially for those new to trading. Allowing substantial losses in your trading positions could result in a cumulative margin call. As someone entering the world of trading, you might be curious about the mechanics of margin calls. I've noticed in brokerages, margin calls are typically expressed as a percentage. How to recognize my margin call and the key factors influencing it are aspects I'm eager to comprehend for effective risk management.
Vitto
Nov 27 2023
So, you're new to trading, and you're wondering about margin calls. Here's the lowdown:
When you trade without a stop loss, especially as a newbie, things can get dicey. If your trades start tanking hard, you might get hit with a margin call. This is like a warning from your broker, saying, "Hey, your losses are getting serious; you need to do something."
Brokers usually express margin calls as a percentage. So, if your losses reach a certain percentage of your initial investment, the alarm bells start ringing.
Now, to know when a margin call is creeping up on you, keep a close eye on your trades. If you see your losses hitting a significant percentage, that's the red flag. (more about margin call : Margin Call: What Is It and How Does It Affect My Trading?)
To dodge the trouble, you might need to tweak your trading strategy, close out some positions, or even throw in some more cash. It's all about playing it smart and managing risks in the unpredictable world of trading.
Jung Oh
Jan 16 2024
Just wanted to inquire about the concept of overtrading, and I find the article quite informative in establishing a connection between margin and various aspects of trading. In the article, there's a discussion on "How to Avoid Margin Calls?" Now that you're familiar with margin calls, you might be wondering how to steer clear of them. The article suggests several measures to prevent a margin call.
And it said that Major currency pairs, such as GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, and EUR/USD, are recommended to trade. These pairs typically have low spreads and high liquidity, making them more straightforward to analyze and minimizing the risk of extreme volatility. Why is it preferable to choose currency pairs with low spreads and high liquidity in addition to being easier to analyze?
Jenny
Jan 20 2024
Lingard
Apr 25 2024
Hey there! So, I came across this article stressing the importance of managing risk to avoid margin calls. It makes total sense—you've got to keep an eye on your trading account's available funds and make smart moves to cut down on losses.
Now, I'm curious: can anyone walk me through some numerical examples of risk management? Let's say I'm planning to start trading with just $100 and using a leverage of 1:500. My strategy is to open positions with only 0.1 lots. How exactly does risk management factor into this scenario?
Leo
Apr 26 2024
Certainly dude! In this scenario, risk management involves calculating the potential loss for each trade and ensuring it aligns with your risk tolerance and account balance.
With a $100 account balance and a leverage of 1:500, you have access to $50,000 in trading capital ($100 * 500). Using 0.1 lots means each pip movement will result in a profit or loss of approximately $1 per micro lot (0.1 lot).
To manage risk effectively, you might consider setting a maximum loss per trade, such as 1% of your account balance. With a $100 account, this would mean risking no more than $1 per trade.
Given that each pip movement with 0.1 lots represents a $1 profit or loss, you could set your stop loss at a maximum of 100 pips away from your entry point to ensure you don't exceed your risk limit of $1 per trade.
This way, even if the trade goes against you and hits your stop loss, you'll only lose $1, which is within your predetermined risk tolerance. By implementing such risk management measures, you can safeguard your trading capital and avoid the risk of a margin call. ( You can read about managing risk in Trading with this article : Managing Risk In Forex Trading)