Learn about blockchain trilemma and why blockchain networks must make trade-offs between them through the following article.
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about digital transactions and trust. However, as blockchain technology expands, new challenges and complexities have emerged. One of these challenges is the concept of "trilemma," which refers to the trade-offs between many things in blockchain networks. In this article, we will explore the concept of trilemma and how it affects the design and implementation of blockchain systems.
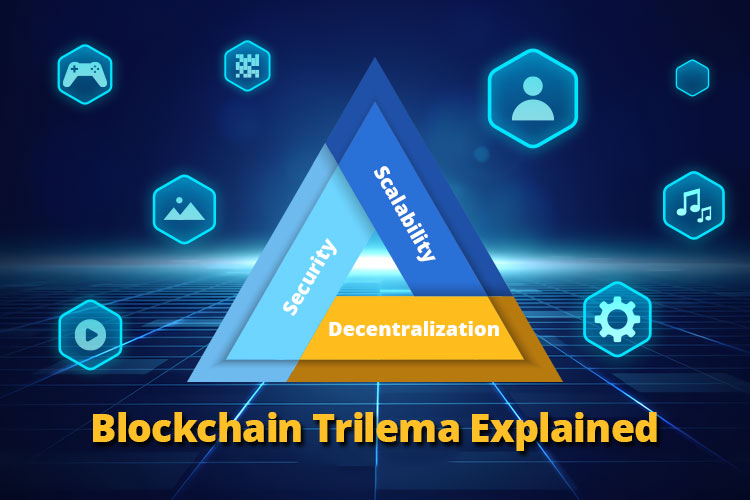
What is Trilemma?
Trilemma is a term that describes the trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization in blockchain networks. These three elements are often considered the pillars of blockchain technology, but they can conflict with one another. Let's break them down one by one:
Security
Security refers to the ability of a blockchain network to protect against malicious actors and ensure the integrity of transactions. This includes protecting against hacking, fraud, and other malicious activities. To achieve high levels of security, blockchain networks often use advanced encryption methods, such as public-key cryptography, to protect the integrity of transactions.
Scalability
Scalability refers to the ability of a blockchain network to handle a large number of transactions and users without becoming bogged down or inefficient. As more users and transactions are added to a blockchain network, the network may become slower and less efficient. Blockchain networks use techniques such as sharding, off-chain transactions, and layer-2 solutions to address this problem to improve scalability.
Decentralization
Decentralization refers to the distribution of power and control within a blockchain network, intending to ensure that no single entity has too much control. This is achieved by distributing the ability to validate transactions among many nodes rather than relying on a single central authority. Decentralization is considered essential for ensuring that a blockchain network is resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Trilemma and Quantum Computing
Quantum computing can significantly impact the trilemma of security, scalability, and decentralization, as it can potentially break the encryption used in many blockchain networks, making them less secure.
Therefore, it is crucial for blockchain development communities to consider the potential impact of quantum computing on the Trilema and work towards designing quantum-resistant blockchain technologies that can balance all three goals.
Trilemma in Practice
In practice, trilemma can manifest in different ways. For example, a blockchain network that prioritizes decentralization may sacrifice scalability in order to ensure that no single entity has too much control. Conversely, a blockchain network that prioritizes scalability may sacrifice decentralization to handle a large number of transactions.
The trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization can also affect the design and implementation of blockchain systems. For example, a blockchain network that prioritizes security may use a consensus mechanism that is more energy-intensive to ensure that the network is resistant to malicious actors. Conversely, a blockchain network that prioritizes scalability may use a consensus mechanism that is less energy-intensive to handle a more significant number of transactions.
Impact on Blockchain Adoption
One of the potential impacts of quantum computing on blockchain technology is its effect on the adoption of blockchain. The security of a blockchain network is one of the most critical factors for its widespread adoption, but it is not the only factor. Other factors, such as scalability and decentralization, also play a role in determining the attractiveness of a blockchain network to users.
Blockchain Trilemma
The Trilemma states that it is impossible to achieve all three goals simultaneously and that a blockchain network must make trade-offs between them.
For example, a blockchain network that prioritizes security may be more resistant to malicious actors but may be less attractive to users who value scalability or decentralization. Conversely, a blockchain network that prioritizes scalability may be more attractive to users who value the ability to handle a large number of transactions. Still, it may be less resistant to malicious actors.
Quantum Computing and Trilemma
The trilemma has become even more complex with the advent of quantum computing. Quantum computing could break the encryption in many blockchain networks, making them less secure. This would make it difficult for a blockchain network to prioritize security while still being attractive to users who value scalability or decentralization.
Furthermore, as quantum computers become more powerful, it may also become increasingly challenging to design blockchain networks that are both scalable and decentralized, as the necessary computational power to maintain a decentralized network may be too great for a quantum computer to handle.
Therefore, it's vital for blockchain development communities to consider the potential impact of quantum computing on their networks and work towards designing quantum-resistant blockchain technologies that can balance all three goals.
Solutions for Trilemma
The Trilema of security, scalability, and decentralization is a significant challenge facing blockchain technology. However, several solutions have been proposed to address this challenge:
Flexible Design
One approach is to design more flexible blockchain networks, allowing users to choose different trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization. This can be achieved by creating a modular design that allows various network components to be customized according to the users' needs. For example, users who prioritize security may use stronger encryption, while users who prioritize scalability may choose sharding.
Consensus Mechanisms
Another approach is to use different consensus mechanisms that can balance the trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization. Other consensus mechanisms have different properties and trade-offs, and choosing the proper mechanism for a particular application can help to balance the Trilemma.
For example, the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism is highly secure but not very scalable. On the other hand, the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism is more scalable but is not as secure as PoW.
Other consensus mechanisms like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) are also used to balance security, scalability, and decentralization trade-offs.
Using a suitable consensus mechanism for a particular application can achieve a good balance between security, scalability, and decentralization.
As the technology of quantum computing develops, it is essential for blockchain communities to consider the impact of quantum computing on the Trilema and work towards finding solutions that balance security, scalability, and decentralization.
Conclusion
Trilemma is a concept that refers to the trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization in blockchain networks. These trade-offs can affect the design and implementation of blockchain systems and the adoption of blockchain technology.
However, it's important to note that trilemma is not an unsolvable problem, and it's possible to find a balance between the three elements. The blockchain industry must continue researching and developing solutions to address the challenges of trilemma and help ensure blockchain technology's long-term success.
Apart from blockchain, you can also store data information in a . How is it different from blockchain? Find the answer here.

 Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS
Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS Free FOREX Virtual Private Server
Free FOREX Virtual Private Server MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500
MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500 Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus
Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024
Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024 Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise
Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise $1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients
$1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus
Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest
Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance
Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance





 Bitcoin
Bitcoin Ethereum
Ethereum Tether
Tether BNB
BNB Solana
Solana USDC
USDC XRP
XRP Dogecoin
Dogecoin Toncoin
Toncoin Cardano
Cardano