While spread betting and CFD trading might sound similar at first, the two are actually very different. Which one is the best for you?
Spread betting and Contract for Difference (CFD) are two common terms fundamentally used in the forex, commodity, and financial industry. The two are often compared directly because they have a number of similarities in terms of functionality and characteristics. But even so, they are considered to be quite different in the eyes of most investors. There are several key distinctions between the two that every investor should know in order to analyze which option is more suitable to them and to the circumstances that they are in.
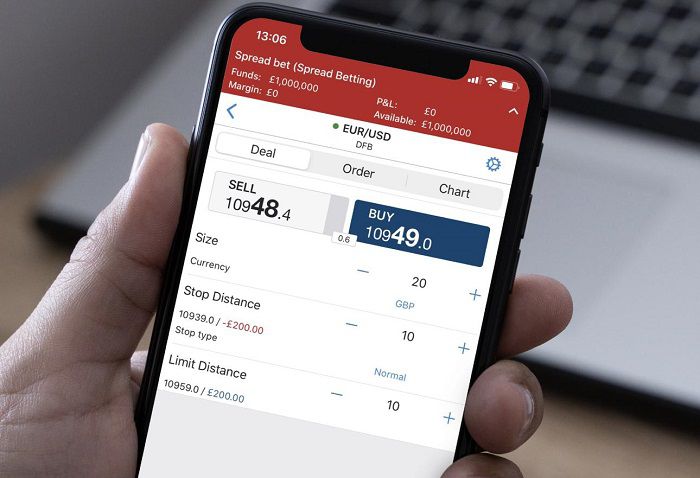
In that case, today we're going to explain in greater detail the differences between spread betting and CFDs as well as why the two products that seem pretty similar are actually very different from one another.
Contents
What is Spread Betting?
Spread betting allows investors to make a simple bet of a certain financial instrument based on the direction they expect the market price to move. A wide variety of financial instruments can be used for spread betting, including forex, stocks, commodities, and more.
When spread betting, the investor should speculate whether the price of an asset like stock or currency pair is more likely to go up or down, and then decide how much they want to bet on it. If they think the price is going to rise, they will open a long buy position. In contrast, if they think the price is going to fall, they will open a short sell position. In addition, investors can choose how much risk they are willing to take.
The amount they want to bet per point of movement in price is perceived as "stake". They will get profit from per point difference between the market price at the close of the trade and the initial buy/sell price when they opened the position, multiplied by their initial stake size.
For example, if you thought a currency pair would rise, you could go long and place a stake at £50 per point of movement. If your prediction was right and the price ended up rising by, let's say, 10 points, then you will get £500 profit from the trade. If the market goes against your favor, your loss will be calculated the same way.
Spread betting is not transferrable between traders, so each trader must trade over the counter directly with the financial institution. Also, spread betting has expiration dates. The bets can be closed at any time before the expiration date and will be closed automatically should the order has not been exercised by the due date.
Spread betting is only available in the UK and Ireland and is considered pretty popular too, mainly because it is commission-free as well as tax-free. But apart from that, spread betting is also very easy in practice and is often considered an effective way to trade in various financial markets with minimal cost and time. You can simply close the bet at any time you want and immediately pocket the profits or limit the losses. Nevertheless, keep in mind that the losses can exceed your deposit amount, making you lose more money than anticipated.
What is CFD Trading?
Contracts for Difference, or in short, CFDs, refer to an agreement or contract between an investor and a financial institution to exchange the difference in the value of a certain asset between the period the contract opens and closes. CFD trading is available to a wide variety of assets including forex, commodities, and shares.
As a financial derivative instrument, CFDs provide an opportunity for investors to take profit from the price movement without having to own the underlying asset. So for example, instead of buying and selling physical gold, an investor can choose to do gold CFD trading and make speculation on whether the price of the asset will rise or fall.
The value of a CFD contract does not derive from the asset's underlying value itself, but only the price change between the trade entry and exit. A CFD contract basically consists of two trades. The first trade creates an open position and will later be closed through a reverse trade at a different price. If the first trade is a buy position, then the second or closing trade is a sell. On the contrary, if the opening trade is a sell, then the closing trade is a buy.
If a trader expects the price to rise, then they will buy the CFD. Once the price rises, the trader will take an offsetting position and sell the contract. The net difference between the buy price and the selling price is then netted together. The result will represent either the gain or loss from the trades and will then be settled through the trader's brokerage account.
Similarly, if the trader speculates that the value will fall, then they will open a sell position. If the price moves lower and the trader closes the trade by purchasing an offsetting trade, the net difference of the buy and sell prices will be cash-settled through their account.
CFDs are transferrable between CFD traders, so the contracts are essentially traded on the open market. Now many brokers even provide Direct Market Access (DMA) to access CFDs. This increases the transparency of the trading process as well as the value of fast trade execution speeds too.
Notable Similarities
The red line that makes spread betting and CFD trading so similar are the facts that both are derivative products. This means investors can use the underlying price to make speculation and gain profit from it without having to physically own the asset. Both options also allow investors the opportunity to take advantage of rising and falling markets, depending on how accurate their predictions are.
In CFD trading, traders would bet whether the value of the underlying asset will go up or down in the future. They would get a choice to open long or short positions based on their predictions. If they expect the price to rise, they will take a long position, while if they expect the price to fall, they will open a short position. In both scenarios, traders may gain some profit from the difference between the closing and buying prices.
Similarly, spread betting also involves investors speculating the spread or the difference between the buy and sell prices quoted by the spread betting company. They would make a long/short position bet and earn profit based on the movement of the asset that is measured in basis points.
That being said, you can choose to use CFD or spread betting if you want to leverage your trades. Each asset will have maximum leverage depending on the broker you use. Also, your broker may or may not allow you to customize the amount of margin when trading CFDs or spread betting.
Main Differences
Here are some of the key differences between spread betting and CFD trading:
Tax
One of the main differences between spread betting and CFD trading is the way they are taxed. Tax law in the UK and Ireland excludes both forms of trading from stamp duty because investors never own the underlying asset. However, CFD trading is subject to capital gains tax, whereas spread betting is not.
This means that if you earn profit from CFD trading, you must pay capital gains tax on the money. You can also use the losses from CFD trading to offset gains from other CFD or other asset trades. You won't have to pay taxes for the gains you get from spread betting, but the losses from spread betting won't be eligible to offset the gains from other trades as well.
Fees
In CFD trading, typically you would have to pay a commission or transaction fee, and not many CFD providers offer commission-free trading. Meanwhile, spread betting is always free of commission fees. However, it's worth noting that both CFD trading and spread betting require you to pay spreads, which is the difference between the bid and ask price of the asset you trade. The amount may vary and fluctuate based on the market's liquidity.
Apart from that, it's also important to understand that when using CFD to trade forex, it would be much easier for you to purchase the contract in the right currency for the pair that you want to speculate on. That is because if you want to speculate currencies other than USD or GBP, you may have to pay conversion fees. In spread betting, you don't have to worry about conversion fees because you can place bets on any currency.
Global Reach
In the UK, both spread betting and CFD trading fall under the regulation of the official financial authority for leveraged products, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). While spread betting is only available in the UK and Ireland, CFD trading is allowed all over the world.
Expiration Date
Spread betting always has a fixed expiry date. Spread bets usually expire at the end of the trading day or on a quarterly basis. Some brokers may allow you to roll over your spread to a new contract, but others may not and will close the bet automatically at the expiry date.
On the other hand, CFD contracts have no expiration dates. Contracts are usually set out for a month at a time, but the broker will automatically roll over the position into a new trade before the old one expires. This means you can open the position for as long as you want, just keep in mind that there might be additional holding fees and increased margin requirements if your trade is losing.
Conclusion
Derivative instruments can be a great way to earn profit without having to spend a lot of money or actually own the underlying asset. As explained above, it's clear that while spread betting and CFD trading may sound similar, the truth is that both are very different in many aspects.
Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. If you live in the UK or Ireland and wish to trade without worrying about tax and commission, then spread betting is excellent for you. Meanwhile, if you're interested in using DMA for shares trading but still getting OTC benefits, then you might want to check out CFD trading.
At the end of the day, what every trader must realize is that derivatives are leveraged products so they are risky and may require advanced skills to take advantage of them.

 Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS
Dedicated FREE FOREX VPS Free FOREX Virtual Private Server
Free FOREX Virtual Private Server MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500
MT4 Demo Contest, Get $500 Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus
Sign Up for an Account, Claim 60% Deposit Bonus Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024
Free MT4/MT5 VPS 2024 Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise
Send E-mail and Get Free Merchandise $1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients
$1K Refer a Friend Bonus for Pepperstone Pro clients Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus
Maximize Your Earnings with 100% Deposit bonus Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest
Trade to Win, $5,000 Monthly Demo Contest Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance
Claim 30% + 15% Deposit Bonus from LiteFinance